The next generation of IP Video Surveillance is with 4K resolution. 4K resolution produces 4 times the quality of Full HD 1080p. Essentially, the amount of pixels produced is 4 times greater than what is seen in a 1080p quality picture ultimately resulting in a greater amount of clarity. This further enhances key analytical features that customers depend on. Analytical features such as tracking multiple entities, facial recognition, license plate recognition, and predictive behaviors are only the initial steps toward a fully-featured surveillance system.
4K resolution frames have greater clarity since the clarity is produced from a larger amount of individual pixels within a captured frame as shown below:
![]()
At first glance at the two referenced images above, the difference is minimal. Now, imagine a scenario when an action is occurring but is not clearly seen and needs to be focused in on more closely. By zooming into a specific part of the viewed image, the difference becomes clear. An HD image instantly becomes blurry and unclear to the viewer since there is a lesser amount of pixels used in order to produce a high-quality image as in 4K.
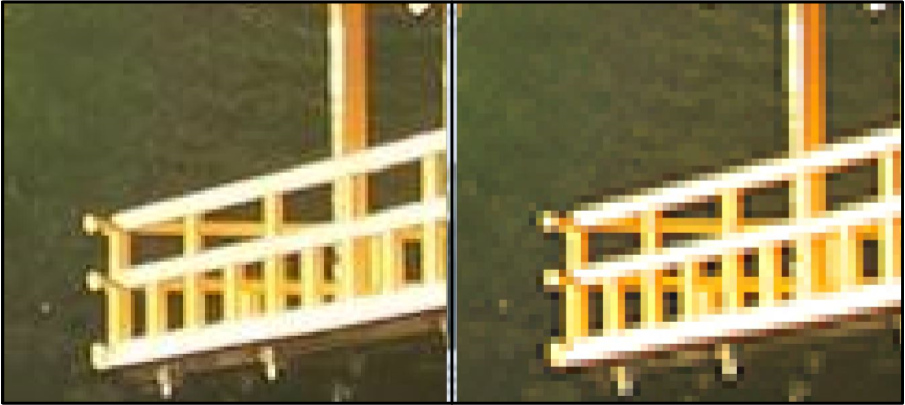
Inherently, this causes the viewer to be unable to depict what the finer details in the image are. Therefore, having a 4K resolution is what creates a higher level of confidence in being able to identify specific objects.
The biggest features in security solutions are advanced analytics. Some features such as facial recognition, license plate recognition, and other items being logged are features that are present today but not clear on all facets. Combining these advanced features with 4K video now gives clarity not only on one piece of an entity, but on all items being presented within the viewed image. This undoubtedly introduces flexibility in delivering the most out of every image captured. All these functions are without a doubt not only beneficial but essential with high-profile environments such as airports, stadiums, government buildings, etc. In order to produce these secure environments, a network has to be ready for this. To be able to produce a next-level security solution requires a strong foundation.
When building an IP video surveillance system with next-generation high-quality imaging, the underlying infrastructure needs to be assessed. Legacy systems are barely able to handle IP cameras that are pushing out 5-8 Mbits/sec. each from a 1080p HD camera. Now, the increase in resolution and imaging needs to have a network that pushes data through at higher rates. IP cameras producing 4K resolution will be experiencing data throughput upwards to 15 Mbits/sec. each and can easily burst to higher rates.
Network switches with Quality of Service features are crucial in developing networks that can push video data at the top of the order to be processed as a top-priority packet. Without Quality of Service, these packets become interleaved with other data and meshed into a giant stream of unorganized packets as a first-come-first-serve basis. This is highly unacceptable with IP Video Surveillance systems. Any loss of transmission of a video packet results in a loss of video that cannot be recovered simply because the action cannot be replicated. In other words, if a crime happens and the captured image data is lost in network transmission, there is now no evidence to show a crime has occurred.
Also, these networks need devices to be able to handle a burst of information as is the nature of IP video surveillance networks. The process of transmitting a piece of captured data changes at a sub-second interval. This means that a brand new captured frame will produce a high amount of data that needs to be transmitted at a sub-second interval resulted from the spike in traffic. Currently, networks are being monitored at a per-second basis, so a high-data frame will not be seen since it is averaged over a one-second stream and observed by the user. Therefore, images resulting in a high amount of data traffic will force network engineers to deploy a network infrastructure that will be able to support a higher amount of traffic. That amount of traffic is attainable through high-quality devices that support technologies such as Gigabit links and 10 Gigabit uplinks to media servers and viewing stations. Without a network foundation properly formed, the only solution is reverting backwards to a standard definition resolution.

